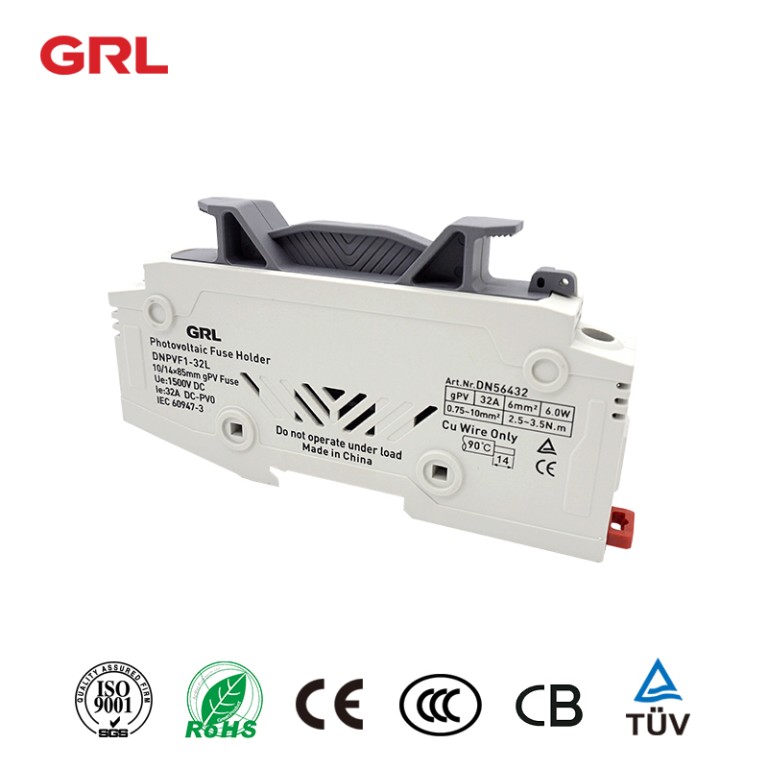
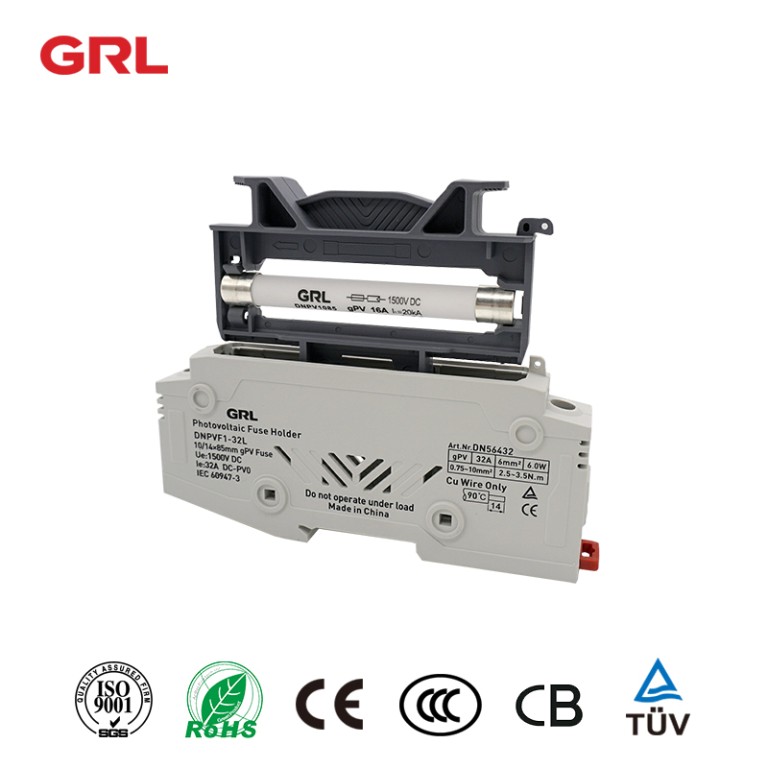
What is the function of a fuse holder?
The function of a fuse holder is to provide a secure and easily accessible location for installing and replacing fuses in an electrical circuit. The fuse holder has two primary functions:
1.Fuse Protection: The main function of a fuse holder is to protect the electrical circuit from excessive current flow. When the current passing through the circuit exceeds the rated capacity of the fuse, the fuse will melt or blow, interrupting the circuit and preventing damage to the circuit components or wiring. The fuse holder holds the fuse in place and ensures proper electrical contact between the fuse and the circuit.
2.Fuse Replacement: Fuse holders allow for easy replacement of fuses when they blow or when maintenance or troubleshooting is required. The holder provides a convenient and safe way to remove the blown fuse and install a new one, minimizing downtime and ensuring the circuit’s protection is restored promptly.
By securely holding the fuse in place and facilitating easy replacement, the fuse holder plays a crucial role in maintaining the safety and functionality of electrical circuits. It helps prevent overloads, short circuits, and potential damage to equipment or wiring, thus safeguarding against electrical hazards and ensuring reliable operation.
Here’s some additional information about the function of a fuse holder:
1.Electrical Contact: Fuse holders ensure proper electrical contact between the fuse and the circuit. They feature terminals or connectors that securely hold the fuse in place while providing a reliable electrical connection. This connection is crucial for the flow of electrical current through the circuit and ensures that the fuse can detect and respond to overcurrent conditions effectively.
2.Mechanical Protection: Fuse holders offer mechanical protection to the fuse. They help prevent accidental contact with the fuse, which could lead to safety hazards or damage to the fuse itself. The holder’s design typically includes features such as covers, enclosures, or shields that protect the fuse from physical impact, dust, moisture, and other environmental factors.
3.Mounting and Installation: Fuse holders come in various configurations to accommodate different mounting requirements. They may be designed for PCB mounting, panel mounting, or in-line installation. The holder’s design allows for secure attachment to the appropriate location, ensuring that the fuse remains in place during operation and minimizing the risk of loose connections or disruptions to the circuit.
4.Fuse Identification: Some fuse holders include labeling or marking features to identify the fuse type, rating, or application. This helps users easily identify the correct replacement fuse and ensures that the circuit is adequately protected. Proper identification of fuses is especially important in applications with multiple fuses or complex electrical systems.
5.Design Flexibility: Fuse holders are available in a wide range of sizes, form factors, and materials to accommodate various fuse types, current ratings, and environmental conditions. This design flexibility allows for compatibility with different applications, enabling users to select the appropriate fuse holder that meets their specific requirements.
Overall, fuse holders provide a crucial role in electrical circuits by protecting against overcurrent conditions, facilitating fuse replacement, ensuring electrical contact, offering mechanical protection, aiding in identification, and providing design flexibility. They are an essential component for maintaining electrical safety and reliability in a wide range of applications, including automotive, industrial, residential, and commercial systems.