Why Miniature Circuit Breakers Can’t Replace Fuses?
Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) and fuses are both electrical protection devices used in electrical circuits to prevent overcurrent and protect electrical equipment from damage. However, they have some differences that make them unique and not always interchangeable. link fuse
Here are some reasons why MCBs cannot always replace fuses:
1.Resettable vs. Non-resettable: MCBs are resettable devices, meaning they can be easily reset after tripping due to an overcurrent event. On the other hand, fuses are non-resettable devices, and once they blow due to an overcurrent event, they need to be replaced. This can be an advantage for fuses in some cases, as they provide a clear indication that an overcurrent event has occurred and the circuit is not protected until the fuse is replaced. In contrast, MCBs can be reset without addressing the underlying issue, potentially leaving the circuit unprotected.
2.Sensitivity: Fuses can be more sensitive to overcurrent events compared to MCBs. Fuses are available in various current ratings and types, and they can have very fast response times to protect sensitive electrical equipment.
MCBs, on the other hand, may have a slightly delayed response time, and their sensitivity may not be as high as some types of fuses. This makes fuses more suitable for certain applications where precise and sensitive protection is required.
3.Application-specific requirements: In some cases, specific electrical codes or regulations may require the use of fuses for certain applications. link fuse
For example, in some industrial or hazardous environments, fuses may be mandated by safety regulations due to their performance characteristics or historical usage. In such cases, MCBs may not be allowed as a replacement for fuses due to regulatory compliance requirements. link fuse
4.Cost: Fuses are generally cheaper compared to MCBs, especially for low-current applications. This cost difference can be a factor in some applications where budget constraints are a consideration. In such cases, replacing fuses with MCBs may not be cost-effective.
5.Existing Infrastructure: In some cases, the electrical infrastructure may be designed or wired specifically for fuses. Replacing fuses with MCBs may require rewiring or modifications to the electrical panel or circuit, which may not be feasible or cost-effective.
6.Reliability: Fuses have been used for a long time and are considered reliable in many applications. They have a simple design with no moving parts, which can make them durable and less prone to failure. MCBs, being more complex devices with mechanical components and electronics, may have a higher probability of failure compared to fuses in some cases. link fuse
In conclusion, while MCBs are widely used and offer many advantages over fuses, they may not always be a direct replacement due to differences in resetability, sensitivity, regulatory compliance, cost, existing infrastructure, and reliability.
The choice between MCBs and fuses should be based on the specific requirements of the electrical circuit and the application, considering factors such as performance, safety, cost, and regulatory compliance. link fuse
It is always recommended to consult a qualified electrician or engineer to determine the appropriate protection device for a particular electrical circuit. link fuse
 Product drawings
Product drawings Fuse Link parameters
Fuse Link parameters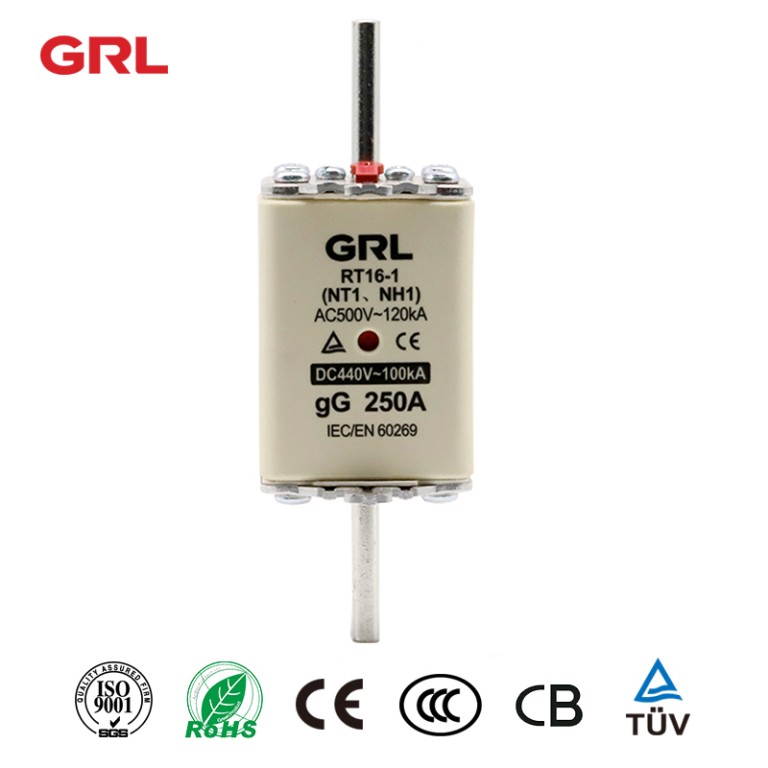
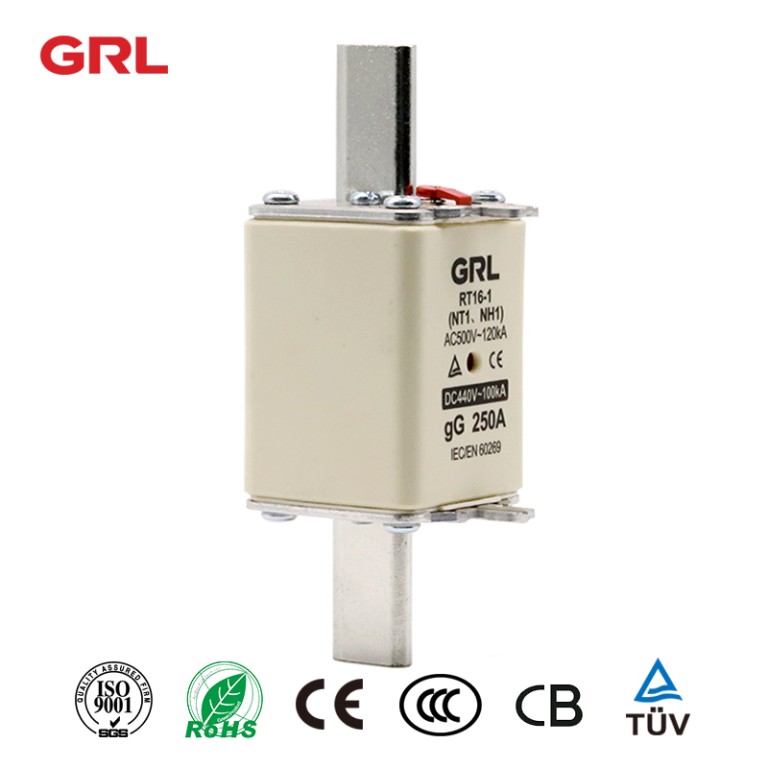
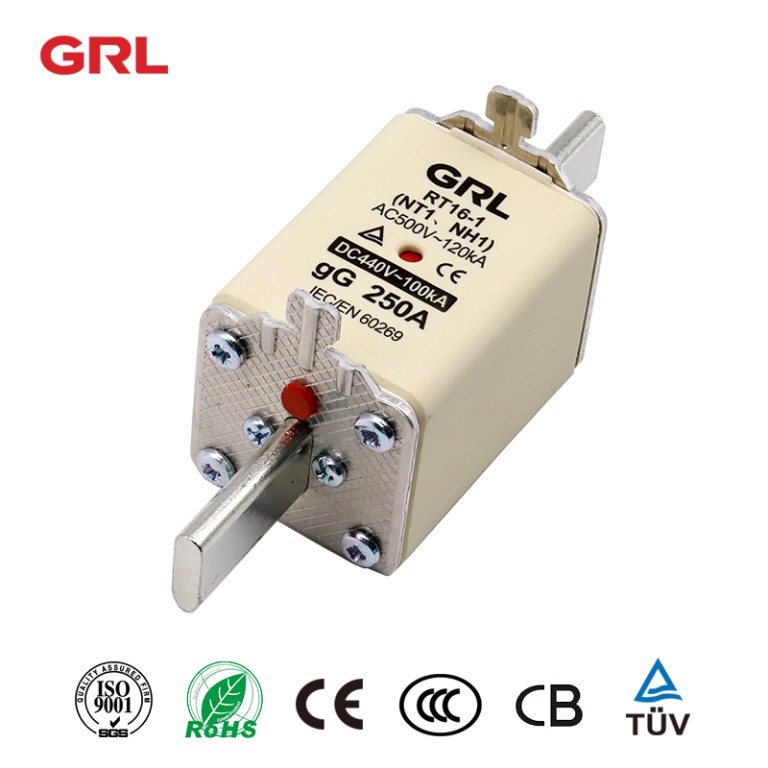
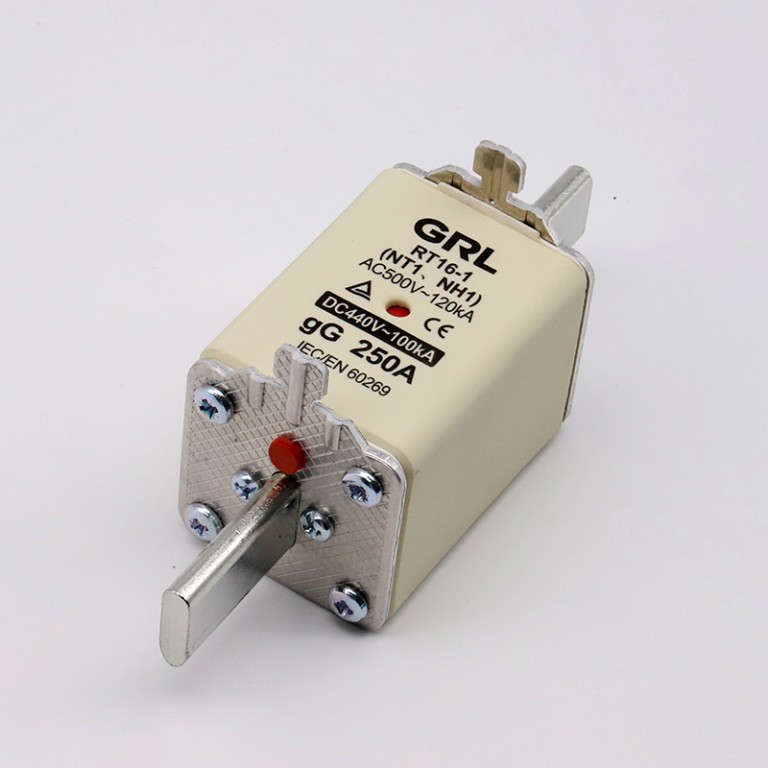
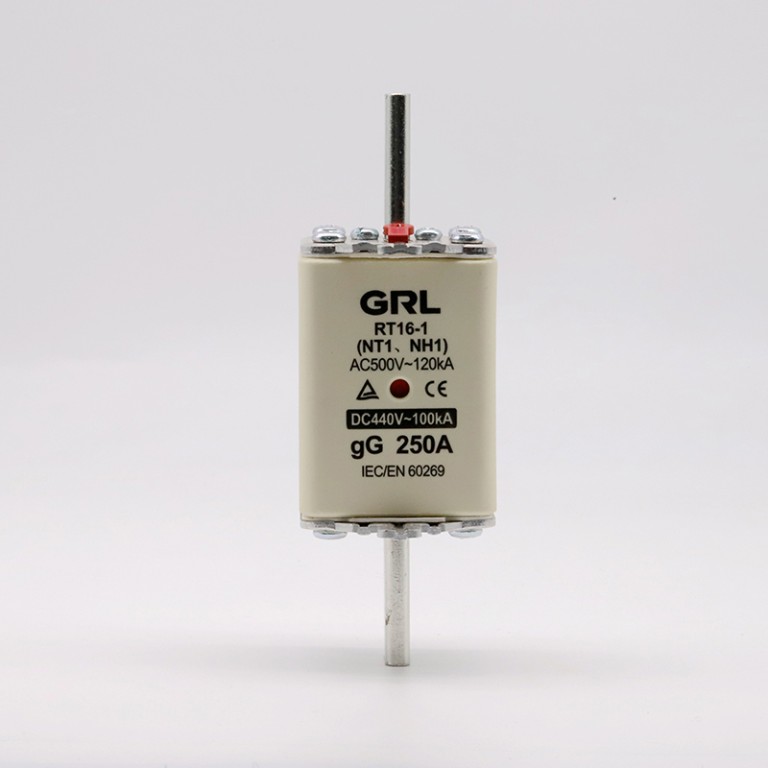











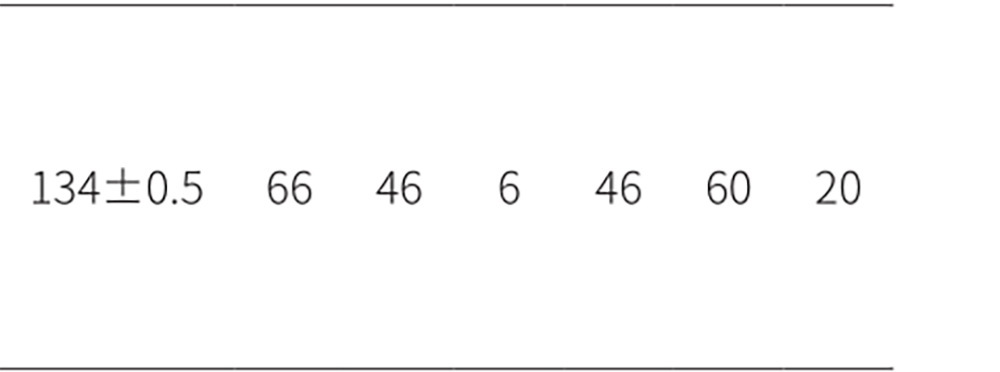 Product drawings
Product drawings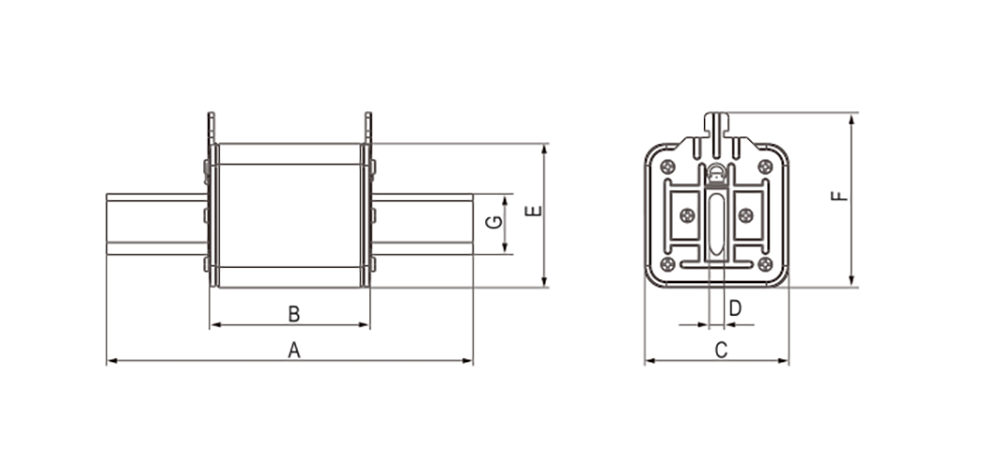 Fuse Link parameters
Fuse Link parameters