Protective characteristics of fuses
Fuses are electrical protection devices that are designed to interrupt the flow of current in a circuit when the current exceeds a predetermined level, known as the rated current or current rating of the fuse. This interruption of current helps to protect electrical equipment and prevent damage caused by overcurrent events.fuse linking
Here are some protective characteristics of fuses:
1.Overcurrent protection: Fuses are primarily used for overcurrent protection, which is one of the most common types of electrical faults. When the current flowing through a fuse exceeds its rated current, the fuse element heats up and melts, causing an interruption in the circuit and stopping the flow of current. This helps to prevent damage to the electrical equipment downstream from the fuse due to excessive current.
2.Short-circuit protection: Fuses also provide short-circuit protection, which is a type of overcurrent event that occurs when there is a direct connection between the supply and return conductors of a circuit, resulting in a very high current flow.
Fuses are designed to quickly interrupt the circuit in the event of a short circuit, preventing potential damage to the circuit and equipment.
3.Thermal protection: Some fuses, such as thermal fuses or thermal cutoffs, are designed to protect against overheating of electrical equipment.
These fuses contain a thermally sensitive element that reacts to excessive temperature by melting and opening the circuit, cutting off the power supply to the equipment. This helps to prevent damage to the equipment due to overheating.fuse linking
4.Arc flash protection: Fuses can also provide protection against arc flashes, which are dangerous and potentially damaging electrical events that can occur when there is a high-energy discharge of electricity between conductors.
Fuses can help interrupt the fault current and limit the duration and energy of the arc flash, reducing the risk of damage to the equipment and injury to personnel.fuse linking
5.Coordination with downstream equipment: Fuses can be coordinated with other protective devices, such as circuit breakers or other fuses, in a circuit to ensure selective coordination. Selective coordination refers to the ability to isolate a fault to a specific portion of the circuit without affecting other parts of the circuit. This helps to minimize downtime and disruption to the electrical system while providing effective protection to the equipment.
6.Simple and reliable operation: Fuses have a simple design with no moving parts, which makes them reliable and robust. They can operate quickly and effectively in response to overcurrent events, providing a predictable and consistent level of protection.
7.Indication of failure: When a fuse blows due to an overcurrent event, it typically melts or breaks, providing a visible indication of failure. This makes it easy to identify and replace the failed fuse, helping to maintain the integrity of the electrical system.
In summary, fuses provide overcurrent, short-circuit, thermal, and arc flash protection, can be coordinated with other protective devices, have simple and reliable operation, and provide indication of failure.fuse linking
These protective characteristics make fuses a widely used and effective means of protecting electrical equipment from damage due to overcurrent events.fuse linking
 Product drawings
Product drawings Fuse Link parameters
Fuse Link parameters
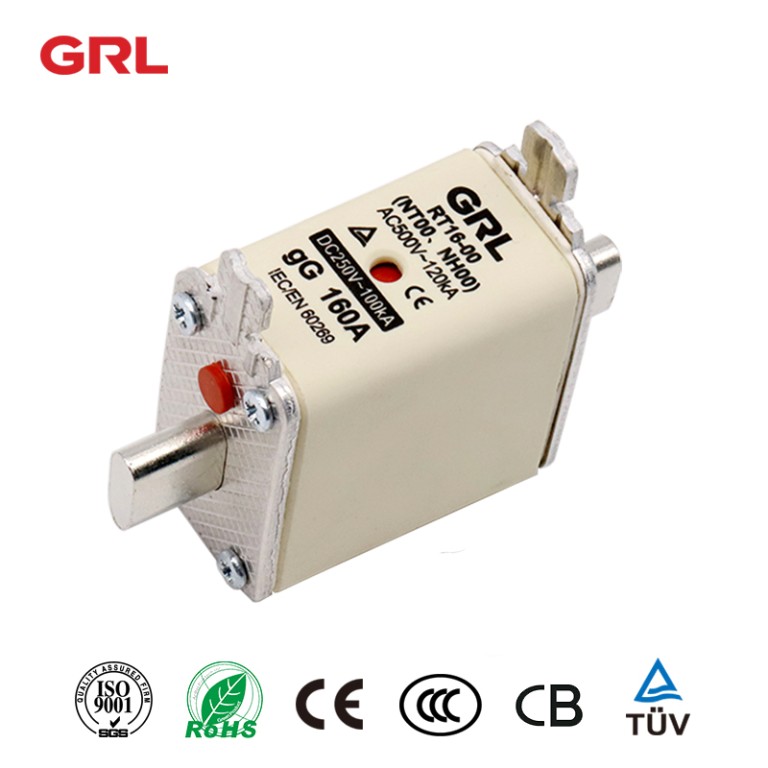
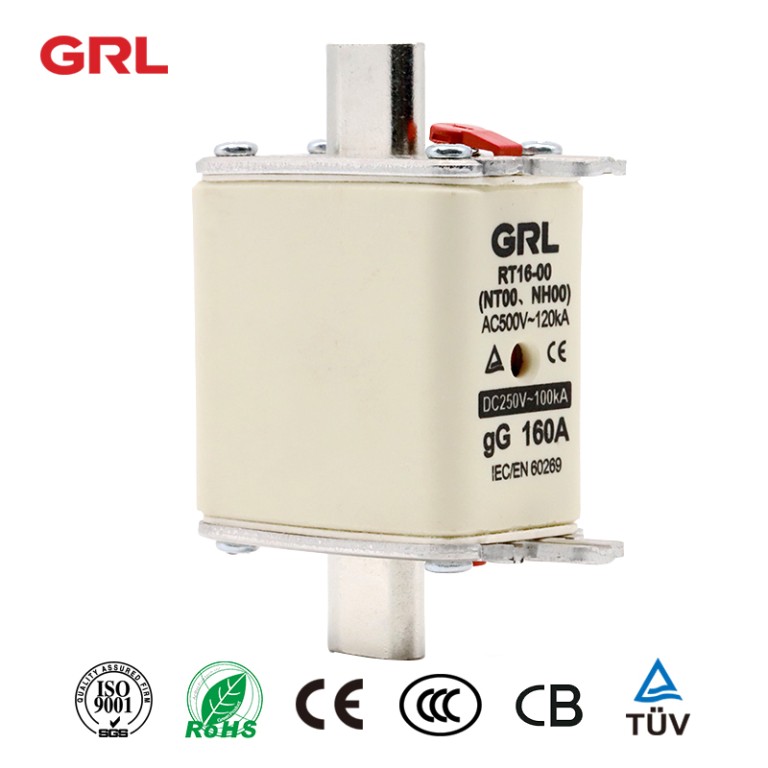
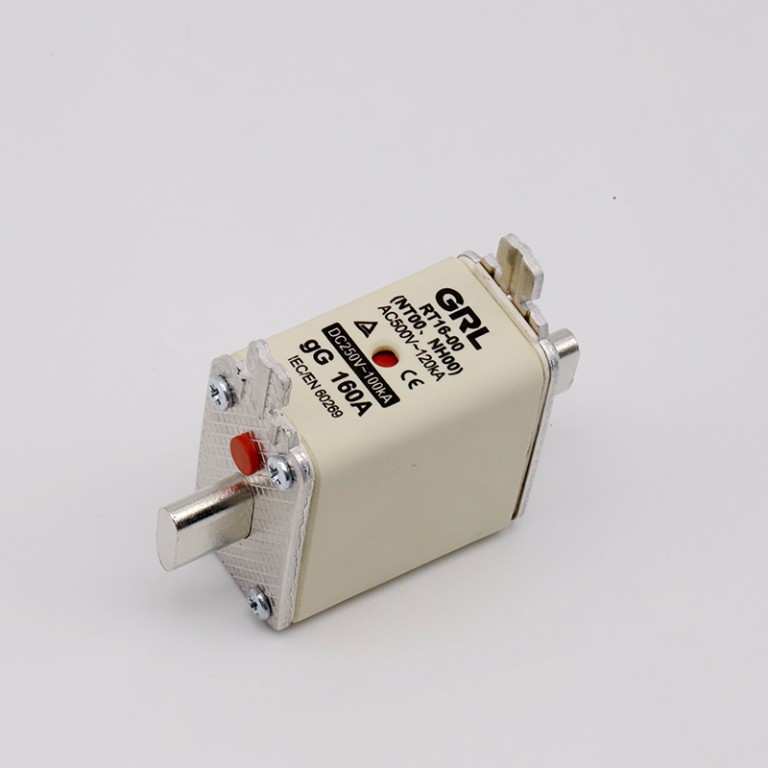
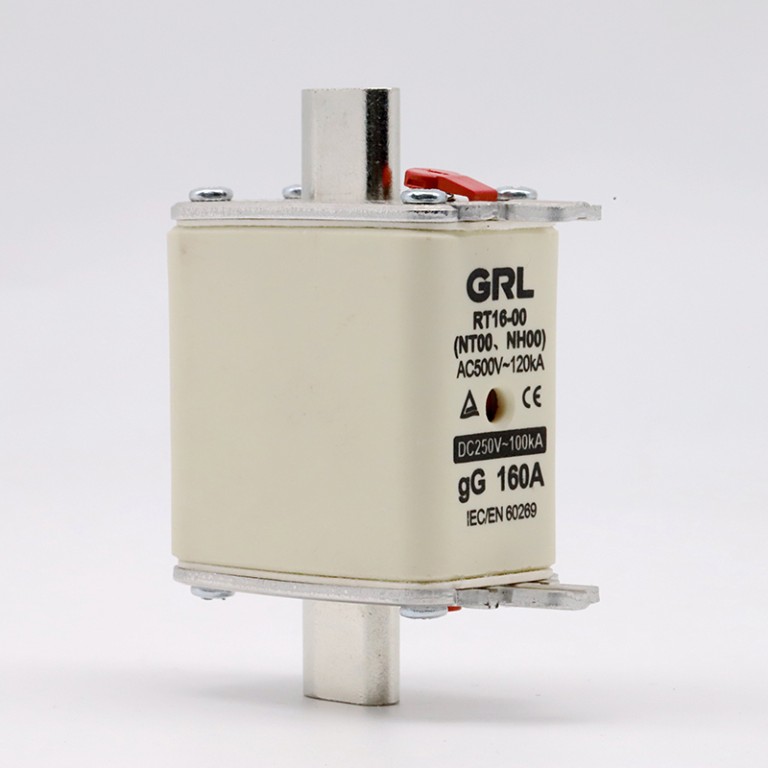










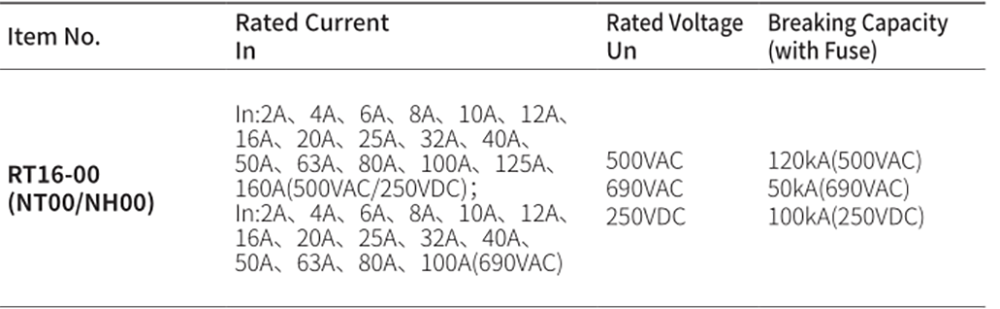
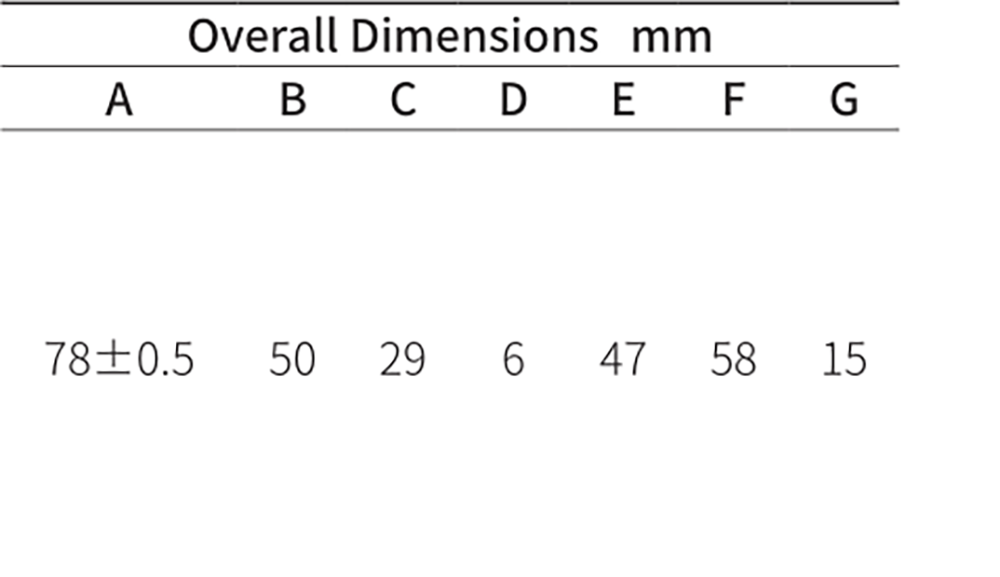 Product drawings
Product drawings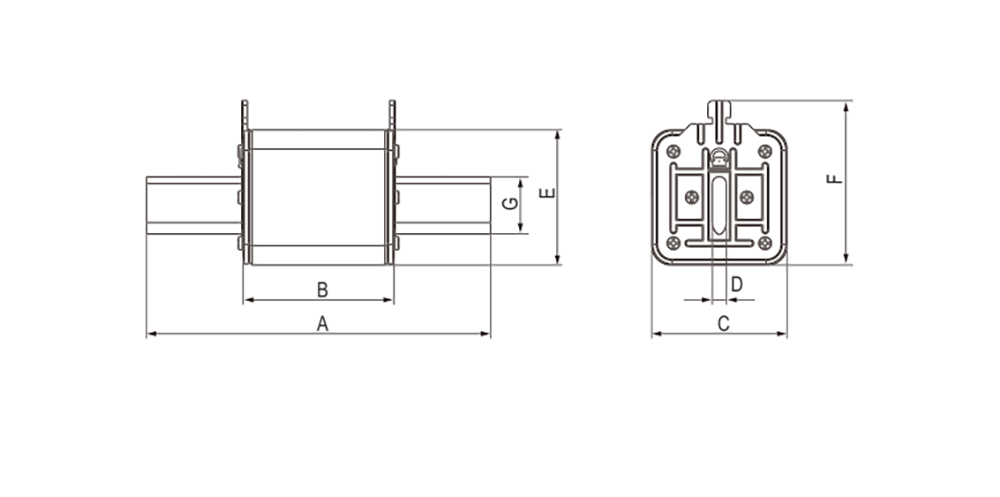 Fuse Link parameters
Fuse Link parameters