What is a Composite Insulator?
A composite insulator is an advanced high-voltage insulation product composed of three main components: an insulating core rod, a silicone rubber shed, and connection fittings. The core rod, made from epoxy resin glass fiber, offers high tensile strength, excellent insulation, and resistance to chemical corrosion, outperforming traditional porcelain in mechanical strength and resilience. Designed for harsh environments, composite insulators are widely used in power transmission and railway electrification systems due to their durability and superior performance under stress.
Composite Insulator Structure
The Composite Insulator consists of three main components:
Insulating Core Rod: Made from epoxy resin glass fiber, it provides structural support, insulation, and mechanical load-bearing capacity. With tensile strength exceeding 60 MPa, it’s significantly stronger than standard steel and up to 8 times stronger than porcelain.
Silicone Rubber Umbrella Cover: Protects the core rod from environmental elements, enhances creepage distance and offers excellent resistance to aging, hydrophobic properties, and high pollution flashover voltage.
High-Quality Connectors: Engineered from special steel, the connectors use a labyrinth design for superior sealing, preventing electrical breakdown.
Our composite insulators leverage advanced technology, such as a computer-controlled crimping process and acoustic emission flaw detection, ensuring reliable and durable performance.
Mechanical Strength: Tensile strength exceeds 60 MPa, making it twice as strong as steel and 5-8 times stronger than porcelain.
Electrical Properties: Offers high pollution flashover voltage, excellent hydrophobicity, and is suitable for use in heavily polluted areas with minimal maintenance.
Environmental Adaptability: Operates between -40°C to +40°C, withstands wind speeds up to 35 m/s, and resists earthquakes up to level 8.
Material Features: The silicone rubber shed incorporates flame retardants and anti-aging agents, ensuring reliable insulation and pollution resistance.
Composite insulators are ideal for:
1、High-Voltage Transmission Lines: Used in systems up to 500kV, providing stable insulation for power lines.
2、Railway Electrification: Meets insulation standards for electrified railway structures, performing well in high-pollution and high-humidity conditions.
3、Industrial and Power Equipment: Offers reliable insulation in substations and switching stations, ensuring equipment safety and operational stability.
Composite Insulators Performance Characteristic
- Lightweight and Compact: They are approximately 1/5 to 1/9 the weight of porcelain insulators of similar grade, making them easier to handle and install.
- High Mechanical and Electrical Strength: These insulators have stable performance and a large safety margin. They can operate safely in heavily polluted areas without the need for regular maintenance.
- Durable and Resistant to Harsh Conditions: Composite insulators resist acid, alkali, and aging, and they have strong sealing to protect against moisture and extreme temperatures.
- Anti-Brittle and Shock-Resistant: Designed to prevent brittle fractures, they perform reliably even under shock and stress.
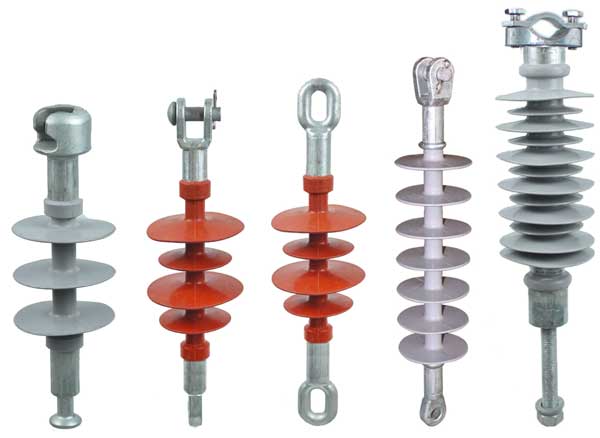

Composite Insulators Types
Our composite insulators come in various models, tailored to different applications:
- FXBW – Rod-type suspension composite insulator
- FPQ – Composite pin insulator
- FZSW – Composite post insulator
- FS – Composite cross-arm insulator
- FCGW – Composite dry wall bushing
- FQB – Wrist composite insulator for electrified railways
- FQX – Suspension composite insulator for electrified railways
- FQJ – Roof composite insulator for electrified roads
Composite Insulators Environmental Adaptability
Temperature Range: -40°C to +40°C
Altitude: Suitable for installations up to 1500 meters above sea level
Max Wind Speed: Withstands up to 35 m/s
Earthquake Resilience: Rated for up to level 8 earthquake intensity
What is the difference between polymer and composite insulators?
Polymer Insulators and Composite Insulators are terms often used interchangeably, but there are some differences, especially in their composition and applications.
1. Material Composition
- Polymer Insulators: Made primarily of polymer materials like silicone rubber or EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer). They have a solid polymer housing over a fiberglass rod, which serves as the core.
- Composite Insulators: These are essentially a type of polymer insulator but with multiple materials combined, hence the term “composite.” A composite insulator typically consists of a fiberglass core, a polymer (like silicone rubber) housing, and metal fittings at both ends. The composite structure provides enhanced performance in mechanical strength and weather resistance.
2. Performance and Durability
- Polymer Insulators: Lightweight, resistant to vandalism, and have excellent hydrophobicity (water-repelling ability), which reduces the risk of flashover in wet conditions. However, their durability may vary depending on the specific polymer used and environmental factors like UV exposure.
- Composite Insulators: Due to their combined materials, composite insulators generally offer higher mechanical strength and longer life spans, especially in environments with high pollution or extreme weather. They are often preferred for outdoor, high-voltage applications where robust durability is critical.
3. Applications
- Polymer Insulators: Commonly used in medium- and high-voltage applications, polymer insulators are often found in transmission and distribution systems, particularly in areas prone to pollution or vandalism.
- Composite Insulators: Ideal for extreme environments, such as high-voltage power lines in highly polluted or coastal regions. Their composite structure provides added protection against environmental stresses, and they’re also frequently used in high-voltage applications like ultra-high-voltage (UHV) transmission systems.
4. Advantages
- Polymer Insulators: Lightweight, easy to handle and install, flexible, and less prone to breakage.
- Composite Insulators: Higher resistance to mechanical stress and environmental conditions, especially suitable for applications requiring enhanced reliability and durability.
In summary, while both types are lightweight, non-ceramic, and widely used in electrical systems, polymer insulators are known for their flexibility and cost-effectiveness, whereas composite insulators are distinguished by their enhanced mechanical strength and durability, particularly suited for high-stress environments.
leave your question
![]()
GRL Electric Co., Ltd. is one of the leading companies in the Middle And High End market of low-voltage electric in China









