Product description
The DNT □ – O1N series semiconductor equipment protection fuse is suitable for AC systems, with a rated voltage of 1000V and a rated current of 160A~1500A. It is used for short-circuit protection of semiconductor components and their complete equipment.
All performance indicators of the product comply with GB/T 13539.4/IEC 60269-4.
Basic parameters of fuse links
| Product model | size | Rated voltage V | Rated current A | Rated breaking capacity kA |
| DNT1-O1N-160 | 1 | AC 1000 | 160 | 100 |
| DNT1-O1N-200 | 200 | |||
| DNT1-O1N-250 | 250 | |||
| DNT1-O1N-315 | 315 | |||
| DNT1-O1N-350 | 350 | |||
| DNT1-O1N-400 | 400 | |||
| DNT1-O1N-450 | 450 | |||
| DNT1-O1N-500 | 500 | |||
| DNT1-O1N-550 | 550 | |||
| DNT1-O1N-630 | 630 | |||
| DNT2-O1N-350 | 2 | 350 | ||
| DNT2-O1N-400 | 400 | |||
| DNT2-O1N-450 | 450 | |||
| DNT2-O1N-500 | 500 | |||
| DNT2-O1N-550 | 550 | |||
| DNT2-O1N-630 | 630 | |||
| DNT2-O1N-710 | 710 | |||
| DNT2-O1N-800 | 800 | |||
| DNT3-O1N-630 | 3 | 630 | ||
| DNT3-O1N-710 | 710 | |||
| DNT3-O1N-800 | 800 | |||
| DNT3-O1N-900 | 900 | |||
| DNT3-O1N-1000 | 1000 | |||
| DNT3-O1N-1100 | 1100 | |||
| DNT3-O1N-1250 | 1250 | |||
| DNT3-O1N-1400 | 1400 | |||
| DNT3-O1N-1500 | 1500 |
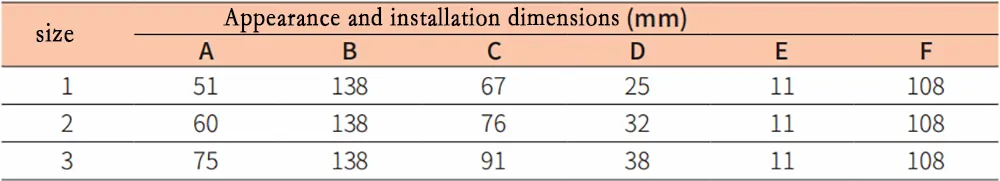
Appearance and installation dimensions
What are the differences between semiconductor fuses used in AC versus DC applications?
Semiconductor fuses, designed to protect sensitive electronic components, exhibit differences when used in alternating current (AC) versus direct current (DC) applications. These differences are primarily due to the distinct characteristics of AC and DC power, which affect the behavior of electrical circuits and, consequently, the design and operation of the fuses used in these circuits.
Differences in Fuse Design and Operation
1.Interrupting Capacity:
AC Fuses: In an AC circuit, the current crosses zero every half-cycle, which naturally helps in extinguishing the arc that forms when a fuse blows. Therefore, AC fuses typically have a lower interrupting capacity compared to DC fuses.
DC Fuses: DC current does not have zero-crossings like AC. Thus, when a DC fuse blows, it’s more challenging to interrupt the current flow and quench the arc. DC fuses need to have a higher interrupting capacity and are often designed with larger gaps and more robust arc-quenching materials.
2.Voltage Ratings:
AC Fuses: The voltage rating for AC fuses usually refers to the maximum RMS voltage the fuse can safely interrupt.
DC Fuses: DC fuses must be rated for the maximum constant voltage they will encounter. Since DC does not have the periodic reduction in voltage like AC, the voltage rating requirements for DC fuses are often more stringent.
Time-Current Characteristics:
The time-current characteristics can differ due to the different ways AC and DC currents affect the thermal and magnetic elements inside the fuse.
Application-Specific Considerations
Inrush Currents: Both AC and DC circuits can experience inrush currents, but the nature and duration of these currents might differ, impacting the choice and design of the fuse. For example, large capacitive loads in DC circuits can lead to significant inrush currents that require special consideration.
Circuit Inductance: The inductance of the circuit plays a more significant role in DC applications, especially in the rapid breaking of the circuit, as inductance can prolong the arc duration.
Physical Size and Construction: DC fuses might be physically larger or constructed differently to handle the sustained arc without degradation, especially in high-voltage applications.
Practical Implications
Interchangeability: Due to these differences, fuses are typically not interchangeable between AC and DC applications. Using an AC-rated fuse in a DC circuit, or vice versa, can lead to inadequate protection and potential safety hazards.
Design and Selection: Engineers must carefully select fuses based on the specific characteristics of their intended application (AC or DC), considering factors like voltage rating, interrupting capacity, and the nature of the load and inrush currents.
In conclusion, while the fundamental purpose of semiconductor fuses in both AC and DC circuits is to protect against overcurrent conditions, the differences in how AC and DC behave significantly impact the design, ratings, and application of these fuses.
Understanding these differences is crucial for the safe and effective use of semiconductor fuses in various electrical and electronic applications.
Click to view grl group company information>>
Click to view grl fuse link product>>
Click to view fuse base product>>
Click to view fuse holder product>>
leave your question
![]()
GRL Electric Co., Ltd. is one of the leading companies in the Middle And High End market of low-voltage electric in China







