Product description
The DNT □ – R1J series semiconductor equipment protection fuse is suitable for AC systems, with a rated voltage of 1300V and a rated current of 160A~1250A.
It is used for short-circuit protection of semiconductor components and their complete equipment.
All performance indicators of the product comply with GB/T 13539.4/IEC 60269-4
Basic parameters of fuse links
| Product model | size | Rated voltage V | Rated current A | Rated breaking capacity kA |
| DNT1-R1J-160 | 1 | AC 1300 | 160 | 100 |
| DNT1-R1J-200 | 200 | |||
| DNT1-R1J-250 | 250 | |||
| DNT1-R1J-315 | 315 | |||
| DNT1-R1J-350 | 350 | |||
| DNT1-R1J-400 | 400 | |||
| DNT1-R1J-450 | 450 | |||
| DNT1-R1J-500 | 500 | |||
| DNT1-R1J-550 | 550 | |||
| DNT2-R1J-350 | 2 | 350 | ||
| DNT2-R1J-400 | 400 | |||
| DNT2-R1J-450 | 450 | |||
| DNT2-R1J-500 | 500 | |||
| DNT2-R1J-550 | 550 | |||
| DNT2-R1J-630 | 630 | |||
| DNT2-R1J-710 | 710 | |||
| DNT2-R1J-800 | 800 | |||
| DNT3-R1J-630 | 3 | 630 | ||
| DNT3-R1J-710 | 710 | |||
| DNT3-R1J-800 | 800 | |||
| DNT3-R1J-900 | 900 | |||
| DNT3-R1J-1000 | 1000 | |||
| DNT3-R1J-1100 | 1100 | |||
| DNT3-R1J-1250 | 1250 |
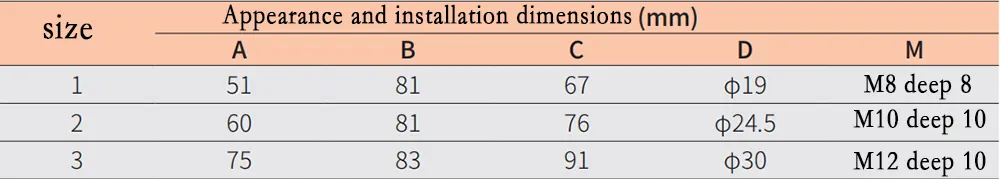
Appearance and installation dimensions
How do environmental factors like temperature or humidity affect the performance of semiconductor fuses?
Environmental factors, particularly temperature and humidity, can significantly affect the performance and reliability of semiconductor fuses. Here’s a closer look at how these factors impact fuse operation:
1.Temperature Effects:
Temperature Coefficient: Most fuse elements have a positive temperature coefficient, meaning their resistance increases with temperature. As the temperature rises, the fuse element heats up, and its resistance increases, which can lead to a reduction in current carrying capacity. In extreme cases, this might cause the fuse to open (blow) under normal current conditions.
Derating: Fuses are often derated for high ambient temperatures. Manufacturers usually provide derating curves that show how the current rating of the fuse should be reduced based on the ambient temperature. Operating a fuse at a higher temperature than it is rated for can significantly shorten its life and increase the likelihood of premature failure.
Thermal Endurance: Long-term exposure to high temperatures can degrade the materials used in the fuse, potentially leading to failures. This degradation can be accelerated by factors such as thermal cycling, where the fuse is repeatedly heated and cooled.
2.Humidity Effects:
Corrosion: High humidity can lead to corrosion of the metal parts in the fuse, particularly the end caps and the fuse element itself. Corrosion can increase the resistance of the fuse element and potentially lead to overheating and failure.
Moisture Ingress: If moisture penetrates the fuse body, it can cause short-circuiting, especially in fuses that are not hermetically sealed. This can be a significant issue in environments where condensation is likely to occur.
Deterioration of Insulation: Humidity can also deteriorate any insulation material in or around the fuse, potentially leading to electrical leakage or short-circuits.
3.Combined Temperature and Humidity Effects:
Accelerated Aging: The combination of high temperature and high humidity can accelerate the aging process of fuses. Materials used in the fuse may deteriorate faster under these conditions, reducing the fuse’s lifespan.
Thermal Shock: Rapid changes in temperature, especially when combined with humidity, can cause thermal shock. This can lead to physical stress and potential damage to the fuse structure.
To mitigate these environmental impacts:
Select Appropriate Fuses: Choose fuses that are designed to operate in the specific environmental conditions they will be exposed to. This might include fuses with higher temperature ratings or those designed to resist corrosion and moisture ingress.
Environmental Protection: Implement environmental control measures, such as maintaining a controlled temperature and humidity level, using enclosures to protect fuses from direct exposure to harsh conditions, or employing conformal coatings to provide additional protection against moisture and contaminants.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection: Regularly inspect fuses for signs of corrosion, damage, or other deterioration due to environmental factors. Replace any fuses that show signs of damage or that have been in service beyond their recommended lifespan.
By understanding and managing the impact of environmental factors like temperature and humidity, the reliability and performance of semiconductor fuses in various applications can be maintained effectively.
Click to view grl group company information>>
Click to view grl fuse link product>>
Click to view fuse base product>>
Click to view fuse holder product>>
leave your question
![]()
GRL Electric Co., Ltd. is one of the leading companies in the Middle And High End market of low-voltage electric in China











